HDMI over IP - How to Send Video Over Ethernet?
What's is HDMI over IP / Internet?
HDMI over IP / Internet is a technology that allows you to transmit and manage HDMI signals over an Ethernet network. Instead of using traditional HDMI cables for point-to-point connections, HDMI over IP encodes HDMI signals into IP data, sends them through network/internet, and then decodes the IP data back to HDMI for display on your screens.
HDMI over IP, also called HDMI over Ethernet, uses an existing ethernet infrastructure to distribute HD video signals from one source to an unlimited number of screens. It can be used in many setups like point-to-point extension, one-to-many distribution, and video wall processing where video can be scaled from different grid layouts. Video signals can be switched from any source to any screen, overcoming distance limitations of traditional CATx video extenders.
HDMI over IP is a way to extend your video signals over long distances. Using HDMI IP Streaming Encoder to transmit lossless compressed h265/h264 video over ethernet enables video extension of resolutions up to 4K@60Hz over the world.
High-end AV over IP systems installed in stadiums, for example, can utilize compression algorithms such as H.264/H.265 to send packetized data over increasingly long distances.
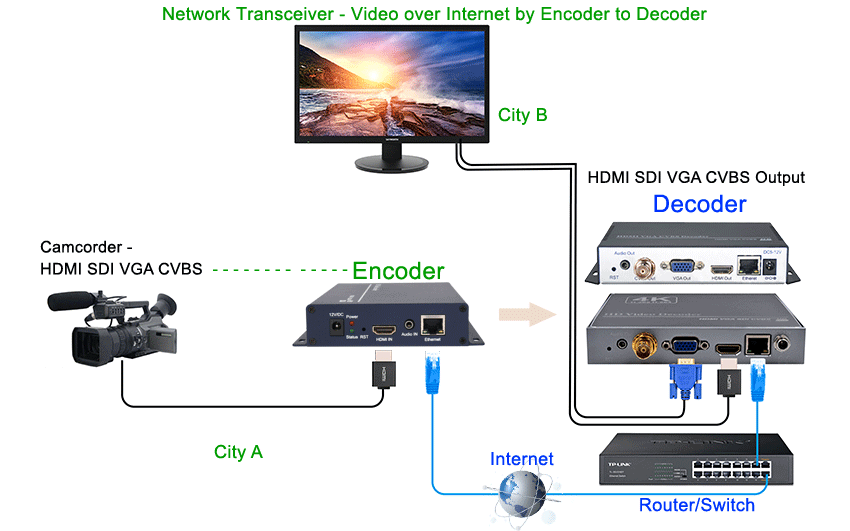
How Does it Work? How to Send Video Over IP?
1. Point-to-Point HDMI: We're all familiar with using HDMI cables for direct connections between devices, such as connecting a desktop computer to a monitor or a Blu-ray player to a TV. However, what if you need to connect a single source device (like a computer or Blu-ray player) to multiple displays simultaneously? HDMI cables alone won't suffice. This is where HDMI over IP comes into play.
2. HDMI over IP Solution: Instead of relying solely on HDMI cables, HDMI over IP encodes HDMI signals into IP data. This IP data is then transmitted via a CAT cable (Ethernet cable) for longer distances, over the world with internet. As the data approaches its destination, a decoder converts the IP data back to HDMI signals, feeding them to the connected displays. This setup allows for greater flexibility, scalability, and extended distances compared to traditional HDMI cables.
3. Encoders and Decoders: The key components in this setup are the HDMI over IP encoder (transmitter) and decoder (receiver). The encoder converts HDMI signals from the source device into IP data, while the decoder performs the reverse process. As you add more encoders and decoders, the system can easily scale up to accommodate numerous devices and displays.
In summary, HDMI over IP provides a flexible and efficient way to distribute HDMI signals across an Ethernet network, making it ideal for scenarios where point-to-point connections fall short.
How and When to Use HDMI Over Ethernet?
Multiroom HDMI / Digital Signage
Multicasting HDMI allows to distribute video and audio to any screen on a signage network. A single transmitter can deliver multimedia to hundreds of displays with no need to run dedicated video links from a back room to displays in lobbies. By combining matrix and video extension solutions, USB extenders, and video and peripheral extension and switching (such as in KVM setups) gives users an almost endless number of configurations for their applications, including touch-interactive signage displays and information and wayfinding displays in retail, healthcare, education, public offces and more.

HDMI to IP Encoders and Decoders / HDMI to IP Streamers
While HDMI to IP encoders allow to convert HDMI video and analog audio input signals to H.264/H.265 for streaming over an IP network connection, HDMI to IP decoders decrypt the compressed IP data stream to display it on a remote output device. These devices are also reffered to as IP streamers when used with specific codecs.
Oupree H.264/H.265 Encoders/Decoders encode/transmit and receive/decode high-quality video over a standard IP network. Because the decoder uses H.265 compression and requires very low bandwidth, it's extremely efficient when decoding full HD video and analog audio. It also supports AAC audio encoding so a high-quaility audio signal can be delivered at low bandwidth requirements.
Factors to Consider When Implementing a Video Distribution Project
Setting a video distribution project is hard work and entails a lot of planning.
What kind of video is being extended?
How many sources and outputs have to be connected?
What video quality and resolutions will be required, and can EDID information be delivered?
Is audio embedded in the video signal or not?
Oupree helps companies design, integrate, and maintain reliable AV solutions for broadcasting, post-production, stadiums & arenas, medical, air traffic control, oil & gas, government & military, and utility industries.