MTU Values on HDMI Video Encoder
The Oupree Video Encoder can adjust its MTU value for improved performance in video encoding.
The MTU (Maximum Transmission Unit) value plays a crucial role in networking and data transmission, particularly in systems like HDMI video encoders that rely on network protocols (e.g., RTP, UDP) for sending video data over IP networks. The MTU value defines the maximum size of a single packet that can be transmitted over the network. The impact of MTU on HDMI video encoders can be understood in terms of how it influences video streaming, latency, and performance.
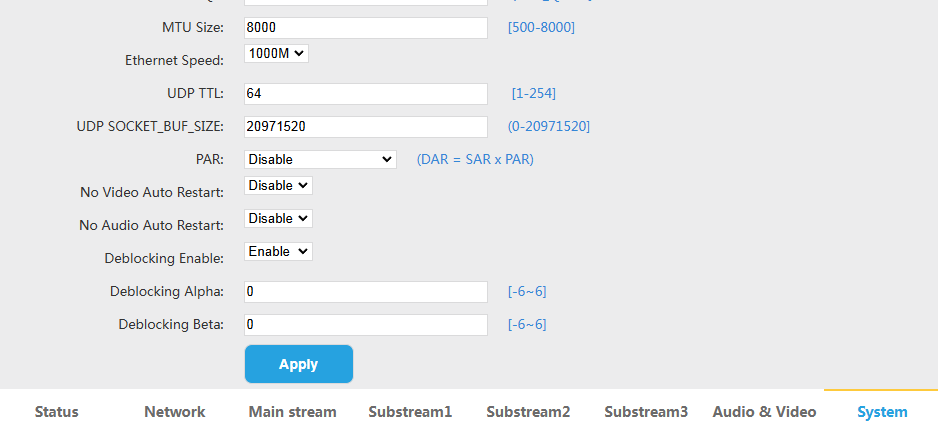
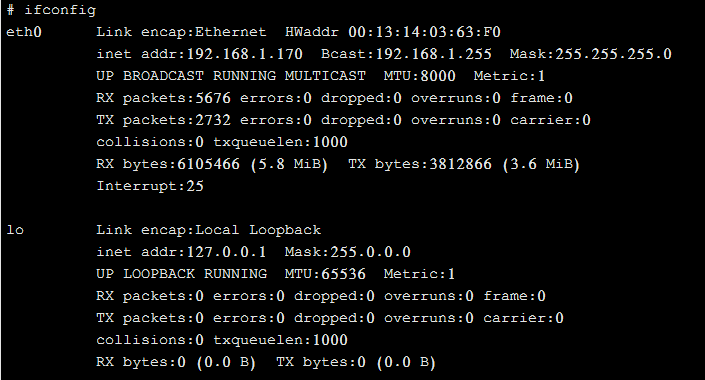
Key Points of MTU and Its Influence on HDMI Video Encoders:
1. Packet Size and Video Data Transmission:
- Video streams, especially in high-definition formats like HDMI, often require large amounts of data to be transmitted. The encoder compresses the video and packages it into network packets for transmission.
- A larger MTU allows the encoder to send more data per packet, reducing the overhead caused by additional headers for smaller packets. This is especially important for video streams, as it reduces network congestion and packet loss.
2. Latency:
- Smaller MTU sizes can result in more frequent packet transmissions, which increases overhead and may introduce latency due to the need for multiple packets to carry the same amount of video data.
- Larger MTU values can reduce the number of packets required, leading to lower overhead and potentially reducing latency in video streaming.
3. Packet Fragmentation:
- If the MTU size of the network link is smaller than the size of the video data packet, fragmentation occurs. This can lead to inefficiencies, as the network has to split the packets into smaller pieces and reassemble them at the receiving end, which can cause delays and additional CPU overhead.
- For optimal performance, it's essential to configure both the encoder and network infrastructure to avoid fragmentation.
4. Network Bandwidth Utilization:
- Larger packets (increased MTU) help maximize bandwidth usage, ensuring that the network is utilized more efficiently for streaming video. However, this assumes the underlying network infrastructure can support larger MTUs without excessive fragmentation.
- If a network device (like a router or switch) doesn’t support large MTU sizes, sending large packets can cause them to be fragmented, reducing the overall performance of the system.
5. Error Handling:
- Smaller MTUs can help with error recovery in the case of lost packets, as the loss of a small packet is less detrimental than the loss of a large one. This is particularly relevant in environments where network stability is variable.
- Larger MTUs increase the risk of packet loss or corruption affecting a larger portion of the data, which may require more frequent retransmissions or error corrections.
6. Optimization for Specific Video Resolutions and Frame Rates:
- High-definition video formats, such as 1080p or 4K, require larger packets to avoid fragmentation, especially with high frame rates or high bitrates. A higher MTU value helps ensure that the video stream is transmitted efficiently and without significant delays.
- The encoder and the network infrastructure should be configured to support these higher MTU values for large video frames.
7. Protocol-Specific Considerations:
- When using protocols like RTP or UDP for video transmission, these protocols have certain header overheads. Larger MTUs reduce the relative overhead of these headers, making the transmission of video data more efficient.
- However, the transport protocol itself (e.g., whether it's UDP, TCP, or RTP) and the specific encoder settings will also influence how well the system performs with different MTU sizes.
Conclusion:
To maximize the performance of an HDMI video encoder in a network environment, it's important to choose an appropriate MTU size based on factors like the network infrastructure, video resolution, frame rate, and expected packet loss. A higher MTU can reduce overhead and improve bandwidth efficiency, but it requires the network and encoder to support it properly. In contrast, smaller MTUs may increase overhead and latency but can be more resilient in less stable networks. Careful tuning and network configuration are key to ensuring smooth and efficient video streaming.